Natural Methods for Reversing Atherosclerosis
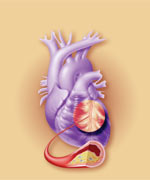 Even when cardiologists aggressively manage their patients’ cholesterol and blood pressure levels, millions of Americans continue to suffer heart attacks and strokes. The reason is that many cardiologists fail to address the key underlying cause of coronary artery disease—that of endothelial dysfunction.
Even when cardiologists aggressively manage their patients’ cholesterol and blood pressure levels, millions of Americans continue to suffer heart attacks and strokes. The reason is that many cardiologists fail to address the key underlying cause of coronary artery disease—that of endothelial dysfunction.
Endothelial dysfunction is the major cause of atherosclerosis—the blockage of arteries that increases the risk of heart attack, stroke, and congestive heart failure. Fortunately, it is never too late to start counteracting this circulatory breakdown, which is often a part of the aging process.
A wealth of research now points to several nutritional agents suchas cocoa polyphenols, pomegranate, and bioavailable superoxide dismutase (SOD) that have been shown to dramatically improve arterial blood flow, helping promote youthful endothelial function and protect against the processes known to damage aging arteries.
The Importance of Endothelial Health
 Very few doctors discuss the importance of endothelial health with their cardiac patients. The endothelium comprises the thin layer of cells that line the interior surfaces of the entire circulatory system including the heart, blood vessels, the lymphatic system, and even the smallest capillaries. Essential to good health, the endothelium maintains uninterrupted circulation by allowing blood to flow smoothly to every part of the body and by participating in blood pressure control. One of its most important functions is the release of nitric oxide, which signals the surrounding smooth muscles of the arteries to relax and dilate, which increases healthy blood flow throughout the body.1
Very few doctors discuss the importance of endothelial health with their cardiac patients. The endothelium comprises the thin layer of cells that line the interior surfaces of the entire circulatory system including the heart, blood vessels, the lymphatic system, and even the smallest capillaries. Essential to good health, the endothelium maintains uninterrupted circulation by allowing blood to flow smoothly to every part of the body and by participating in blood pressure control. One of its most important functions is the release of nitric oxide, which signals the surrounding smooth muscles of the arteries to relax and dilate, which increases healthy blood flow throughout the body.1
But harmful oxidative stress, such as that which occurs in hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, diabetes, cigarette smoking, and the aging process itself inactivates nitric oxide, thereby contributing to endothelial dysfunction.2
Damage occurs when the endothelium’s structural integrity is compromised and is no longer able to protect the artery walls against the infiltration of cholesterol, triglycerides, and low-density lipoprotein (LDL). Thus, endothelial dysfunction is one of the first steps in the creation of atherosclerosis—the buildup of arterial plaque that elevates the risk for heart attack, stroke, and congestive heart failure.3
 Unfortunately, as we age, our body continually loses optimal endothelial function. A research study published in the journal Gerontology that examined healthy people showed that endothelial function declines with increasing age.4 Even worse, some research has shown that the development of endothelial dysfunction can begin as early as the teenage years.5 Cardiovascular researchers believe the endothelium has an “enormous yet largely untapped diagnostic and therapeutic potential,”6 which is why a better understanding of endothelial dysfunction may help to prevent or delay deadly cardiovascular events. As scientists continue to unravel the numerous causes of heart disease and atherosclerosis, the importance of preserving endothelial health is gaining appreciation.7
Unfortunately, as we age, our body continually loses optimal endothelial function. A research study published in the journal Gerontology that examined healthy people showed that endothelial function declines with increasing age.4 Even worse, some research has shown that the development of endothelial dysfunction can begin as early as the teenage years.5 Cardiovascular researchers believe the endothelium has an “enormous yet largely untapped diagnostic and therapeutic potential,”6 which is why a better understanding of endothelial dysfunction may help to prevent or delay deadly cardiovascular events. As scientists continue to unravel the numerous causes of heart disease and atherosclerosis, the importance of preserving endothelial health is gaining appreciation.7
Fortunately, researchers have identified several innovative nutritional ingredients that appear to enhance endothelial health. Among them are cocoa, pomegranate, and a bioavailable formulation of superoxide dismutase (SOD) called GliSODin®. In studies published in peer-reviewed journals, these substances have been shown to have properties that protect against endothelial dysfunction, while helping reverse clinical markers of arterial plaque.
Cocoa: A Natural Antioxidant that Preserves Cardiovascular Health
 Centuries before European confectioners processed the beans of the Theobroma cacao plant to make a confection we call “chocolate,” cocoa was used in Mexico and parts of Latin America in its powdered form for medicinal purposes. Recent studies in medical journals have found that cocoa may actually be cardioprotective, and a new study showed it may even be able to reverse the effects of endothelial dysfunction by improving the dilation of blood vessels.8
Centuries before European confectioners processed the beans of the Theobroma cacao plant to make a confection we call “chocolate,” cocoa was used in Mexico and parts of Latin America in its powdered form for medicinal purposes. Recent studies in medical journals have found that cocoa may actually be cardioprotective, and a new study showed it may even be able to reverse the effects of endothelial dysfunction by improving the dilation of blood vessels.8
Cocoa has a high concentration of polyphenol compounds, specifically a class of natural compounds called flavonoids. Scientists have identified several cocoa flavanols, including epicatechin and catechin, which can benefit circulatory health. Cocoa flavanols improve endothelial function by enhancing nitric oxide bioactivity,9 increasing blood flow,9 reducing the tendency of blood clot formation,10 reducing moderately high blood pressure,11 and helping LDL resist oxidation, which may prevent the buildup of atherosclerotic plaque in artery walls.12
A study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology8 found that giving flavanol-rich cocoa to diabetic patients improved their vascular function. In an editorial accompanying the research report, another team of scientists noted that the study provides “sizable evidence that cocoa flavanols have a positive effect on the health of the arteries.”13
Scientists at the Department of Nutrition, University of California-Davis also found that cocoa had a beneficial effect on cardiovascular health. Their 2006 study in the Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology found that “consuming flavanol-rich cocoa and cocoa-based products can improve endothelial function in both compromised and otherwise normal, healthy individuals.” Six weeks of cocoa consumption increased brachial artery hyperemic blood flow by up to 76% compared with baseline values. Additionally, cocoa consumption decreased levels of a blood marker associated with the progressive formation of atherosclerotic lesions, signaling protection against the accumulation of dangerous plaque.14
 Important research from the Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics demonstrated a possible biochemical mechanism through which cocoa may help preserve vascular health. Using a double-blind, crossover study design, scientists found that adults who consumed cocoa demonstrated decreased arginase enzymatic activity. Inhibition of arginase is reported to improve endothelial-dependent vasodilation by making more arginine available. Thus this study suggests that cocoa may help promote healthy blood vessel dilation and optimal circulation.15
Important research from the Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics demonstrated a possible biochemical mechanism through which cocoa may help preserve vascular health. Using a double-blind, crossover study design, scientists found that adults who consumed cocoa demonstrated decreased arginase enzymatic activity. Inhibition of arginase is reported to improve endothelial-dependent vasodilation by making more arginine available. Thus this study suggests that cocoa may help promote healthy blood vessel dilation and optimal circulation.15
A recent clinical trial examined the effects of dark chocolate including liquid cocoa on endothelial function and blood pressure in overweight adults. Consumption of dark chocolate or liquid cocoa improved endothelial function and decreased blood pressure. Sugar-free cocoa produced greater improvements in endothelial function, compared with regular cocoa containing sugar. This led the study authors to conclude that sugar may decrease cocoa’s benefits for endothelial health and blood pressure, and that sugar-free cocoa preparations may offer superior benefits.16
These findings offer powerful support for cocoa’s role in maintaining optimal endothelial health.
Pomegranate: An Ancient Fruit that Can Reverse Atherosclerosis
 Studies have found that pomegranate has powerful antioxidant properties that appear to protect the heart and blood vessels.17 Pomegranate juice may have anti-atherosclerotic properties, slowing the progression of arterial plaques.18 Most promising may be the results from studies showing that pomegranate juice improves stress-induced ischemia in patients who already had cardiovascular disease and atherosclerosis.19 Pomegranate even shows benefits in reducing systolic blood pressure.18 Punicalagins, tannins, and anthocyanins are the major components in pomegranate that are responsible for its antioxidant and cardiovascular health benefits.
Studies have found that pomegranate has powerful antioxidant properties that appear to protect the heart and blood vessels.17 Pomegranate juice may have anti-atherosclerotic properties, slowing the progression of arterial plaques.18 Most promising may be the results from studies showing that pomegranate juice improves stress-induced ischemia in patients who already had cardiovascular disease and atherosclerosis.19 Pomegranate even shows benefits in reducing systolic blood pressure.18 Punicalagins, tannins, and anthocyanins are the major components in pomegranate that are responsible for its antioxidant and cardiovascular health benefits.
One of pomegranate’s key mechanisms for supporting cardiovascular health is its ability to modulate nitric oxide activity. In endothelial cells, pomegranate enhances the bioactivity of nitric oxide synthase, an enzyme that generates nitric oxide.17 Pomegranate’s antioxidant effects also help protect nitric oxide against oxidative destruction, thus ensuring its availability for essential vessel-protective functions.20,21
In a small, controlled study published in the journal Clinical Nutrition, 10 patients with atherosclerosis and carotid artery stenosis (narrowing of the main arteries in the neck that supply blood to the brain) were able to reverse the effects of carotid atherosclerosis by supplementing their diet with pomegranate juice each day for one year. Carotid artery atherosclerosis (measured as carotid intima-media thickness) decreased by a remarkable 30% in those who consumed pomegranate juice daily, while it increased by 9% in patients who did not consume pomegranate juice. In those who consumed pomegranate, total antioxidant status was increased by 130%, while blood serum levels of LDL basal oxidative state and LDL susceptibility to oxidation were both significantly reduced, by 90% and 59%, respectively. Systolic blood pressure was reduced by 12% after one year of pomegranate juice consumption, but was not further reduced after two additional years of pomegranate juice consumption. The researchers suggested the improvement in the patients’ cardiovascular health “could be related to the potent antioxidant characteristics of pomegranate juice polyphenols.”18
 A study reported in the prestigious American Journal of Cardiology also demonstrated the benefits of pomegranate juice in people with atherosclerosis. In a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study, 45 patients with stable coronary heart disease who suffered from stress-induced ischemia (reduced blood supply to the heart muscle caused by atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries) were randomly assigned to drink pomegranate juice (eight ounces daily) or a placebo each day. Participants underwent several cardiac diagnostic tests at the beginning and at the end of the trial. After three months, the measurable extent of stress-induced ischemia decreased in the pomegranate group, but increased in the control group. This benefit was observed without changes in cardiac medications, blood sugar, hemoglobin A1c, or weight. The researchers concluded that daily consumption of pomegranate juice may improve stress-induced myocardial ischemia in patients with coronary heart disease.19
A study reported in the prestigious American Journal of Cardiology also demonstrated the benefits of pomegranate juice in people with atherosclerosis. In a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study, 45 patients with stable coronary heart disease who suffered from stress-induced ischemia (reduced blood supply to the heart muscle caused by atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries) were randomly assigned to drink pomegranate juice (eight ounces daily) or a placebo each day. Participants underwent several cardiac diagnostic tests at the beginning and at the end of the trial. After three months, the measurable extent of stress-induced ischemia decreased in the pomegranate group, but increased in the control group. This benefit was observed without changes in cardiac medications, blood sugar, hemoglobin A1c, or weight. The researchers concluded that daily consumption of pomegranate juice may improve stress-induced myocardial ischemia in patients with coronary heart disease.19
These studies demonstrate that pomegranate offers important cardiovascular health benefits for patients who already suffer from atherosclerosis and endothelial dysfunction, and suggest that pomegranate may similarly help preserve cardiovascular well-being in healthy people.
-
Many cardiologists fail to address one of the key underlying causes of atherosclerosis—endothelial dysfunction.
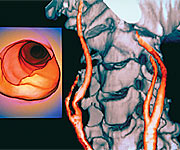
- Endothelial dysfunction occurs when the structure and function of the cells lining blood vessels become impaired, diminishing healthy blood flow and leading to the buildup of atherosclerotic plaque.
- Hypertension, smoking, and the aging process itself increase the risk for endothelial dysfunction, which in turn increases the risk for heart attack, stroke, and heart failure.
- Cocoa polyphenols improve endothelial function, enhance blood flow, improve LDL’s resistance to oxidation, and modulate blood pressure. Sugar-free cocoa appears to offer superior benefits to preparations that include sugar.
- Pomegranate helps enhance cardiovascular health by supporting nitric oxide activity, reversing atherosclerotic plaque buildup, and improving blood pressure.
-
Diminished levels of the antioxidant enzyme SOD have been linked with cardiovascular disease. A bioavailable formulation called GliSODin® helps boost the body’s levels of SOD while reversing the buildup of atherosclerotic plaque.
SOD: The Body’s Own Antioxidant
 One of the most important enzymes in the body, superoxide dismutase (SOD) was identified by scientists only 40 years ago.22 SOD is the major antioxidant enzyme that provides the body’s first enzymatic step in the defense system against oxidative stress. As a natural antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent, SOD maintains cellular health by activating cellular repair. Most importantly, SOD plays a pivotal role in protecting tissues from damage by oxidant stress by removing or neutralizing the superoxide radical that has been implicated in many disease states including inflammatory diseases, cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases, and cancer.23
One of the most important enzymes in the body, superoxide dismutase (SOD) was identified by scientists only 40 years ago.22 SOD is the major antioxidant enzyme that provides the body’s first enzymatic step in the defense system against oxidative stress. As a natural antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent, SOD maintains cellular health by activating cellular repair. Most importantly, SOD plays a pivotal role in protecting tissues from damage by oxidant stress by removing or neutralizing the superoxide radical that has been implicated in many disease states including inflammatory diseases, cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases, and cancer.23
A study published in the journal Circulation in 2002 found that in patients with chronic heart failure, endothelial-bound SOD activity was substantially reduced. Diminished SOD levels were closely linked with increased vascular oxidative stress, which contributes to endothelial dysfunction in chronic heart failure.24
SOD also has important anti-aging qualities. Mice lacking a form of SOD die from oxidative stress within days of birth25 and those bred without a second type of SOD are highly susceptible to age-related problems like cataracts.26 Unfortunately, SOD levels decline as we age—reducing our defense against free radicals just at the time when the body’s free radical activity is increased.27
Therefore it makes sense for scientists to look for a way to increase SOD levels in the body to be able to benefit from this important antioxidant.28 Food scientists found that a certain species of melon naturally contained high levels of SOD. Supplementing with this melon extract, however, failed to boost SOD levels in the body because acids and enzymes in the digestive system broke down the SOD before it could be assimilated into the body. After much trial and error, scientists combined SOD with gliadin protein from wheat extract to create an orally effective delivery system called GliSODin® that is capable of increasing the body’s levels of protective SOD. This new bioavailable form of SOD passes through the stomach intact, then continues to the intestines, where it is absorbed into the bloodstream.
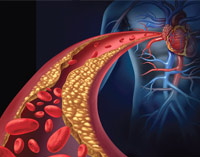 A clinical study confirms GliSODin®’s ability to provide antioxidant protection to the body. For 28 days, scientists supplemented animals with either standardized melon SOD or with standardized melon SOD extract combined with gliadin (GliSODin®). The two groups were evaluated for various biomarkers of oxidative stress. Animals supplemented with GliSODin® showed a significant elevation in circulating antioxidant enzyme activity, correlated with an increased resistance of red blood cells to oxidative stress-induced hemolysis (rupture). In contrast, animals supplemented with melon SOD alone showed no change in their level of antioxidant protection.29
A clinical study confirms GliSODin®’s ability to provide antioxidant protection to the body. For 28 days, scientists supplemented animals with either standardized melon SOD or with standardized melon SOD extract combined with gliadin (GliSODin®). The two groups were evaluated for various biomarkers of oxidative stress. Animals supplemented with GliSODin® showed a significant elevation in circulating antioxidant enzyme activity, correlated with an increased resistance of red blood cells to oxidative stress-induced hemolysis (rupture). In contrast, animals supplemented with melon SOD alone showed no change in their level of antioxidant protection.29
Another study powerfully demonstrated GliSODin®’s protective effects on the cardiovascular system. A group of doctors at a preventive medicine society in Paris administered GliSODin® to adults aged 30-60 years old at risk for cardiovascular disease based on genetic factors, blood chemistry, blood pressure, body mass index (BMI), and a history of cigarette smoking. Remarkably, the physicians found that two years of supplementation with GliSODin® actually reversed the buildup of atherosclerotic plaque in the carotid arteries, as determined by ultrasound measurements of carotid intima-media thickness. Additionally, GliSODin® supplementation increased antioxidant capacity in the subjects.28
Together, these findings suggest that GliSODin® may offer a practical strategy for maintaining youthful levels of protective SOD as we age, which may help prevent and even reverse endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis.
Conclusion
Preserving optimal endothelial function is essential to maintaining smooth flow of blood through the arteries and preventing the accumulation of atherosclerotic plaque that can contribute to heart attack, stroke, and other cardiovascular diseases. Powerful, natural antioxidant sources like cocoa and pomegranate have been shown to enhance cardiovascular health. In some studies, pomegranate and cocoa have been shown to limit or reverse atherosclerosis, lower high blood pressure, and improve endothelial function in people with the most serious arterial problems, including heart disease and diabetes. Scientists continue to research superoxide dismutase, the body’s own powerful antioxidant. Now that it is bioavailable as GliSODin® to supplement the body’s naturally declining levels, there is another powerful anti-aging strategy to maintain healthy endothelial function and help prevent or reverse atherosclerosis.
Material used with permission of Life Extension. All rights reserved.
1. Nitenberg A. Hypertension, endothelial dysfunction and cardiovascular risk. Arch Mal Coeur Vaiss. 2006 Oct;99(10):915-21.
2. Cai H, Harrison DG. Endothelial dysfunction in cardiovascular diseases: the role of oxidant stress. Circ Res. 2000 Nov 10;87(10):840-4.
3. Brocq ML, Leslie SJ, Milliken P, Megson IL. Endothelial dysfunction: from molecular mechanisms to measurement, clinical implications, and therapeutic opportunities. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2008 Sep;10(9):1631-74.
4. Yavuz BB, Yavuz B, Sener DD, et al. Advanced age is associated with endothelial dysfunction in healthy elderly subjects. Gerontology. 2008;54(3):153-6.
5. Aggoun Y, Farpour-Lambert NJ, Marchand LM, Golay E, Maggio AB, Beghetti M. Impaired endothelial and smooth muscle functions and arterial stiffness appear before puberty in obese children and are associated with elevated ambulatory blood pressure. Eur Heart J. 2008 Mar;29(6):792-9.
6. Aird WC. Phenotypic heterogeneity of the endothelium: I. Structure, function, and mechanisms. Circ Res. 2007 Feb 2;100(2):158-73.
7. Münzel T, Sinning C, Post F, Warnholtz A, Schulz E. Pathophysiology, diagnosis and prognostic implications of endothelial dysfunction. Ann Med. 2008;40(3):180-96.
8. Balzer J, Rassaf T, Heiss C, et al. Sustained benefits in vascular function through flavanol-containing cocoa in medicated diabetic patients a double-masked, randomized, controlled trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008 Jun 3;51(22):2141-9.
9. Heiss C, Dejam A, Kleinbongard P, et al. Vascular effects of cocoa rich in flavan-3-ols. JAMA. 2003 Aug 27;290(8):1030-1.
10. Holt RR, Schramm DD, Keen CL, Lazarus SA, Schmitz HH. Chocolate consumption and platelet function. JAMA. 2002 May 1;287(17):2212-3.
11. Grassi D, Necozione S, Lippi C, et al. Cocoa reduces blood pressure and insulin resistance and improves endothelium-dependent vasodilation in hypertensives. Hypertension. 2005 Aug;46(2):398-405.
12. Baba S, Natsume M, Yasuda A, et al. Plasma LDL and HDL cholesterol and oxidized LDL concentrations are altered in normo- and hypercholesterolemic humans after intake of different levels of cocoa powder. J Nutr. 2007 Jun;137(6):1436-41.
13. Campia U, Panza JA. Flavanol-rich cocoa a promising new dietary intervention to reduce cardiovascular risk in type 2 diabetes? J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008 Jun 3;51(22):2150-2.
14. Wang-Polagruto JF, Villablanca AC, Polagruto JA, et al. Chronic consumption of flavanol-rich cocoa improves endothelial function and decreases vascular cell adhesion molecule in hypercholesterolemic postmenopausal women. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2006;47 Suppl 2S177-86.
15. Schnorr O, Brossette T, Momma TY, et al. Cocoa flavanols lower vascular arginase activity in human endothelial cells in vitro and in erythrocytes in vivo. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2008 Mar 6.
16. Faridi Z, Njike VY, Dutta S, Ali A, Katz DL. Acute dark chocolate and cocoa ingestion and endothelial function: a randomized controlled crossover trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2008 Jul;88(1):58-63.
17. de Nigris F, Williams-Ignarro S, Botti C, Sica V, Ignarro LJ, Napoli C. Pomegranate juice reduces oxidized low-density lipoprotein downregulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in human coronary endothelial cells. Nitric Oxide. 2006 Nov;15(3):259-63.
18. Aviram M, Rosenblat M, Gaitini D, et al. Pomegranate juice consumption for 3 years by patients with carotid artery stenosis reduces common carotid intima-media thickness, blood pressure and LDL oxidation. Clin Nutr. 2004 Jun;23(3):423-33.
19. Sumner MD, Elliott-Eller M, Weidner G, et al. Effects of pomegranate juice consumption on myocardial perfusion in patients with coronary heart disease. Am J Cardiol. 2005 Sep 15;96(6):810-4.
20. Ignarro LJ, Byrns RE, Sumi D, de Nigris F, Napoli C. Pomegranate juice protects nitric oxide against oxidative destruction and enhances the biological actions of nitric oxide. Nitric Oxide. 2006 Sep;15(2):93-102.
21. de Nigris F, Williams-Ignarro S, Sica V, et al. Effects of a pomegranate fruit extract rich in punicalagin on oxidation-sensitive genes and eNOS activity at sites of perturbed shear stress and atherogenesis. Cardiovasc Res. 2007 Jan 15;73(2):414-23.
22. McCord JM, Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutase. An enzymic function for erythrocuprein (hemocuprein). J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 25;244(22):6049-55.
23. McCord JM, Edeas MA. SOD, oxidative stress and human pathologies: a brief history and a future vision. Biomed Pharmacother. 2005 May;59(4):139-42.
24. Landmesser U, Spiekermann S, Dikalov S, et al. Vascular oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction in patients with chronic heart failure: role of xanthine-oxidase and extracellular superoxide dismutase. Circulation. 2002 Dec 10;106(24):3073-8.
25. Melov S. Mitochondrial oxidative stress. Physiologic consequences and potential for a role in aging. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000 Jun;908:219-25.
26. Behndig A, Karlsson K, Reaume AG, Sentman ML, Marklund SL. In vitro photochemical cataract in mice lacking copper-zinc superoxide dismutase. Free Radic Biol Med. 2001 Sep 15;31(6):738-44.
27. Pansarasa O, Castagna L, Colombi B, Vecchiet J, Felzani G, Marzatico F. Age and sex differences in human skeletal muscle: role of reactive oxygen species. Free Radic Res. 2000 Sep;33(3):287-93.
28. Cloarec M, Caillard P, Provost JC, et al. GliSODin, a vegetal sod with gliadin, as preventative agent vs. atherosclerosis, as confirmed with carotid ultrasound-B imaging. Eur Ann Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007 Feb;39(2):45-50.
29. Vouldoukis I, Conti M, Krauss P, et al. Supplementation with gliadin-combined plant superoxide dismutase extract promotes antioxidant defences and protects against oxidative stress. Phytother Res. 2004 Dec;18(12):957-62.
What causes atherosclerosis?
Endothelial dysfunction is the leading cause of atherosclerosis, a blockage in the arteries that increases the risk of heart attack, stroke and congestive heart failure. Fortunately, it's never too late to start preventing these cardiovascular diseases and atherosclerosis, often part of the aging process. Maintaining optimal endothelial function is important for maintaining smooth blood flow through the arteries and preventing the accumulation of atherosclerotic plaques that can contribute to heart attacks, strokes and other cardiovascular diseases.
Is atherosclerosis reversible?
Numerous studies have shown that several nutritional factors such as cocoa polyphenols, pomegranate and bioavailable superoxide dismutase (SOD) can dramatically improve blood flow in the artery, support healthy endothelial function and protect against arterial damage caused by aging and thus prevent a disease which is atherosclerosis. One study found that pomegranate and cocoa reduced or reversed atherosclerosis, lowered high blood pressure, and improved endothelial function in people with the most serious artery problems, including heart disease and diabetes. With the advent of the bioavailable supplement GliSODin® to naturally replenish declining SOD levels in the body, we have another effective anti-aging strategy to maintain healthy endothelial function and help prevent or reverse atherosclerotic processes.





