Carnosine, Cataracts, And Visual Clarity
 Cataracts cause about half of all cases of blindness worldwide.1,2
Cataracts cause about half of all cases of blindness worldwide.1,2
By age 80, more than half of all Americans will have cataracts, or will have undergone surgery to remove them.3
Researchers have been investigating two different but related forms of the nutrient carnosine to help slow the development of cataracts as well as improve visual performance of cataract-affected eyes.
A new study illustrates the ability of oral carnosine in capsule form to preserve normal structure of proteins in the lens of the eye—an action that may slow or prevent the development of vision-impairing cataracts.4
The study shows that carnosine works through several interrelated mechanisms that help protect against the underlying changes caused by aging that lead to cataracts.4
In addition, human studies have found that a derivative of carnosine, N-acetylcarnosine, when used as an eye drop, can induce improvements in visual performance of cataract-affected eyes.5,6
Many readers of this magazine have been using a high-potency carnosine supplement (500-1,000 mg/day) since we introduced it in 2000.
A number of others also use eye drops that deliver N-acetylcarnosine directly to the eye lens where cataracts occur.
Based on both established and recent science, there is now a two-part strategy of using both carnosine and N-acetylcarnosine to help reduce the risk of cataracts.
 Cataracts, which are cloudy collections of misfolded protein molecules that accumulate in the lens, are a leading cause of vision loss and blindness in older adults.
Cataracts, which are cloudy collections of misfolded protein molecules that accumulate in the lens, are a leading cause of vision loss and blindness in older adults.- Among the primary underlying causes of cataracts are oxidative stress and glycation of the delicate proteins that naturally maintain the lens in a state of crystalline clarity.
- Carnosine has potent anti-glycation and free radical-reducing properties.
- A new study sheds light on mechanisms by which carnosine protects lens proteins to prevent cataracts and their progression.
- Human, animal, and lab studies show that carnosine can prevent the protein damage that produces cataracts, but also has the capability of reversing them, leading to the possibility of the first therapy to slow cataract progression.
Eye Lens Protector
 Cataracts are cloudy spots in the otherwise crystal-clear lens of the eye that are formed when lens tissues break down, or when lens proteins clump together.4,7 They cause blurred vision, a faded appearance of colors, and increased sensitivity to glare and bright lights.7
Cataracts are cloudy spots in the otherwise crystal-clear lens of the eye that are formed when lens tissues break down, or when lens proteins clump together.4,7 They cause blurred vision, a faded appearance of colors, and increased sensitivity to glare and bright lights.7
Cataracts were once thought to be an inevitable consequence of aging. Today, we recognize that cataracts have several interrelated causes.
That makes a multitargeted nutrient like carnosine attractive for fighting the structural defects that manifest clinically as vision-robbing cataracts.8
Carnosine is a combination of two amino acids, alanine and histidine. Your body makes some of its own carnosine. It is found in higher concentrations in muscle, the brain—and in lenses of the eyes.9-12
A dietary source of carnosine is red meat, something that many health-conscious people seek to reduce or avoid altogether. Even red-meat eaters, however, only have protective carnosine levels part of the day. That's because the amount of carnosine in meat is rapidly degraded by carnosinase enzymes in your body.13
Scientists are discovering that the use of oral and topical forms of carnosine can help reduce the risk of cataracts.
As you'll read next, carnosine possesses unique mechanisms that guard against structural changes that lead to cataract formation.14-17
How Oral Carnosine Prevents Cataracts
 As we age, the cumulative impact of oxidant stress and protein degradation18-29 distorts our delicate eye lenses—and helps explain the increase in cataracts.
As we age, the cumulative impact of oxidant stress and protein degradation18-29 distorts our delicate eye lenses—and helps explain the increase in cataracts.
A factor for the development of age-related cataracts is protein misfolding and clumping—hallmarks of cataract formation.29
A new laboratory study shows that carnosine works through several mechanisms that help protect against cataracts.
The researchers discovered the following new findings:4
• The presence of carnosine largely prevented the accumulation of distorted and dysfunctional lens proteins.
• Carnosine achieved these effects in part by restoring the protective function of the lens protein, alpha-crystallin. These crystallins are present at high concentrations in the eye lens, and preserving their proper structure and arrangement is an important factor in keeping the lens clear.
Carnosine reduced lens protein instability and breakdown. Ultimately—and most importantly—carnosine prevented the development of lens cloudiness, the ultimate outcome of cataracts.
This new scientific study hails the multitargeted functions of carnosine, and suggests new mechanisms by which carnosine may prevent glycation- and oxidative stress-related cataract formation.4
Cataracts, Glycation, and Carnosine
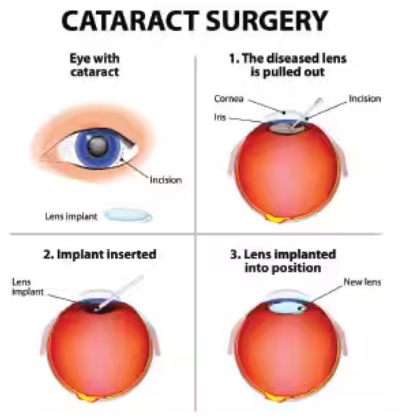 Glycation is one of the underlying causes of cataracts.29 It is also one of the basic processes (along with oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and DNA damage) that hastens the aging process in all cells, tissues, and organs.27,28
Glycation is one of the underlying causes of cataracts.29 It is also one of the basic processes (along with oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and DNA damage) that hastens the aging process in all cells, tissues, and organs.27,28
Diabetes is the classic example of the adverse impact of glycation. Diabetes is a grimly accurate model of accelerated aging.30-33 People with diabetes suffer from the features associated with normal aging, but at a much faster rate than seen in nondiabetic individuals.
One of the common denominators for diabetes and normal aging is the glycation of proteins and the resulting deterioration of their function.27 This means that fighting glycation everywhere in the body is a direct and important way to decelerate aging.
Perhaps nowhere is the impact of glycation on accelerated aging as apparent as it is in the eye lens, the normally crystal-clear portal that focuses light on the retina.29
Glycation of lens proteins occurs in both diabetic and nondiabetic people, although diabetics experience cataracts much earlier than nondiabetics.19-27
Carnosine is a potent antiglycation agent and oxidative-stress reducer. One animal study of cataracts showed its ability to reduce levels of glycated lens proteins, prevent the loss of protective enzymes, and, ultimately, to delay the clouding of the lens.17
One important laboratory study showed that carnosine prevented the lens protein crystallin from clumping together into dense, opaque fibrils. Carnosine was then found to simultaneously restore crystallin's ability to positively impact other proteins and prevent them from clumping together.15
Even more promising, carnosine has now been shown to disassemble those dense opaque clumps of crystallin, thereby restoring lens transparency in animal lenses in culture.15
It is important to note that some of the studies presented here discuss the well-known antiglycation properties of oral carnosine supplementation in cataract prevention.
As you are about to learn, topical application of a derivative form of carnosine called N-acetylcarnosine has been shown to penetrate the lens of the eye and help maintain more youthful structural eye lens clarity.
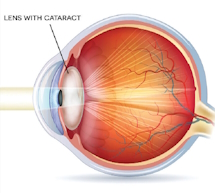 In order to understand why carnosine is so beneficial, it's helpful to understand how cataracts form to begin with.
In order to understand why carnosine is so beneficial, it's helpful to understand how cataracts form to begin with.
Cataracts are opaque collections of deformed proteins that accumulate within the clear lens of the eye.4,36
All proteins rely closely on their exquisitely-folded molecular structure for their function. Misfolded proteins don't work properly, and misfolded lens proteins become opaque and unable to transmit light, thereby forming a cataract.37,38
An important factor in protein misfolding in the lens is nonenzymatic glycation. In this process, sugars become chemically bound to amino acids, proteins, and other essential biomolecules, distorting their structure, which contributes to protein misfolding.4,39-42
Specialized "chaperone" proteins called crystallins normally help prevent protein unfolding in the lens. But when crystallins themselves undergo glycation, they lose this protective function. This essentially removes the last line of defense, and allows cataracts to form even faster.23,38,40,41
The most recent study of carnosine in cataracts shows us that, by slowing glycation-induced unfolding of lens proteins, carnosine can help prevent cataract formation.4
Human Studies on N-Acetylcarnosine Eye Drops
 As we have seen, carnosine can play an important role as it relates to normal structural changes that occur in the eye over time. When carnosine is applied as an eye drop, it can benefit the surface cornea, but does not penetrate the eye lens.
As we have seen, carnosine can play an important role as it relates to normal structural changes that occur in the eye over time. When carnosine is applied as an eye drop, it can benefit the surface cornea, but does not penetrate the eye lens.
N-acetylcarnosine, however, can penetrate the front chamber of the eye and subsequently undergo conversion into carnosine.34 N-acetylcarnosine eye drops may thus be a useful delivery vehicle to boost carnosine levels beyond the cornea into the front chamber of the eye and the eye lens.
Human studies have demonstrated that N-acetyl-carnosine 1% eye drops lead to improvements in cataracts and visual performance of cataract-affected eyes.5,6
Specifically, the studies demonstrated improvement in overall light transmission, glare sensitivity, and, most importantly, visual sharpness.5,6
Improvements in glare sensitivity are particularly relevant for older adults who drive. Glare sensitivity can be very dangerous because it produces the characteristic halos around bright lights, which can confuse drivers and contribute to accidents.
One study showed that N-acetylcarnosine 1% eye drops given to older drivers improved visual clarity and reduced glare sensitivity at red and green targets.35 For best results, use carnosine as early as possible, since its specialty lies in preventing, rather than treating, cataracts.
 Cataracts are among the most common visual disorders, causing about half of all cases of blindness worldwide.1,2
Cataracts are among the most common visual disorders, causing about half of all cases of blindness worldwide.1,2
There are many risk factors for cataracts, including diabetes, smoking, alcohol, and sunlight exposure.3 Glycation plays an important role in the development of cataracts. Studies show that reducing or reversing glycation with oral carnosine and topical N-acetylcarnosine eye drops can slow cataract formation.4,8,17,43-46
Symptoms of cataracts include blurred vision, a faded appearance of colors, increased sensitivity to glare and bright lights, and diminished night vision.3
As a result, many cataract sufferers have trouble with basic visual functions such as driving, reading, or recognizing faces.47 Additionally, there is now evidence that cataract-induced vision problems can increase the risk of depression and even of falling in older people.48
Anyone who is experiencing these symptoms should see their physician or optometrist for an eye examination, which is the only way of diagnosing cataracts.3
Summary
 By age 80, a majority of Americans will have cataracts or have undergone cataract surgery.
By age 80, a majority of Americans will have cataracts or have undergone cataract surgery.
Cataracts are dull, opaque collections of misfolded proteins that accumulate within the lens of the eye, blocking light and blurring vision.
Protein glycation is a destructive process involved in the production of the dense protein clumps that form cataracts. This has led to an explosion of interest in bioactive molecules capable of preventing or even reversing glycation in an effort to preserve clear vision into our advanced years.
Carnosine has now been shown to preserve the proper structure and arrangement of lens proteins, preventing loss of lens crystallinity under laboratory and real-world conditions. One of the main ways it accomplishes this is through its ability to fight glycation, which is a critical factor in cataract formation.
N-acetylcarnosine has long been used as a 1% stabilizing agent in eye drops that contain FDA-approved lubricating agents.
A number of people use these eye drops daily for their multifaceted benefits.
To maintain continuous carnosine blood levels, take a supplement that provides 500 mg of carnosine twice daily.
The reason it's important to take 500 mg of oral carnosine twice a day is that carnosinase enzymes degrade even higher-potency (500 mg) carnosine within 12 hours of ingestion.13
Material used with permission of Life Extension. All rights reserved.
- Available at: http://www.cureblindness.org/cause. Accessed October 3, 2017.
- Available at: https://medlineplus.gov/magazine/issues/summer08/articles/summer08pg14-15.html. Accessed October 3, 2017.
- Available at: https://www.nei.nih.gov/health/cataract/cataract_facts. Accessed 27 May, 2017.
- Javadi S, Yousefi R, Hosseinkhani S, et al. Protective effects of carnosine on dehydroascorbate-induced structural alteration and opacity of lens crystallins: important implications of carnosine pleiotropic functions to combat cataractogenesis. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2017;35(8):1766-84.
- Babizhayev MA, Deyev AI, Yermakova VN, et al. Efficacy of N-acetylcarnosine in the treatment of cataracts. Drugs R D. 2002;3(2): 87-103.
- Babizhayev MA, Deyev AI, Yermakova VN, et al. N-Acetylcarnosine, a natural histidine-containing dipeptide, as a potent ophthalmic drug in treatment of human cataracts. Peptides. 2001;22(6):979-94.
- Available at: http://www.medicinenet.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=2645. Accessed October 4, 2017.
- Babizhayev MA, Micans P, Guiotto A, et al. N-acetylcarnosine lubricant eyedrops possess all-in-one universal antioxidant protective effects of L-carnosine in aqueous and lipid membrane environments, aldehyde scavenging, and transglycation activities inherent to cataracts: a clinical study of the new vision-saving drug N-acetylcarnosine eyedrop therapy in a database population of over 50,500 patients. Am J Ther. 2009;16(6):517-33.
- Miyaji T, Sato M, Maemura H, et al. Expression profiles of carnosine synthesis-related genes in mice after ingestion of carnosine or ss-alanine. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2012;9(1):15.
- Trexler ET, Smith-Ryan AE, Stout JR, et al. International society of sports nutrition position stand: Beta-Alanine. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2015;12:30.
- Boldyrev AA, Dupin AM, Bunin A, et al. The antioxidative properties of carnosine, a natural histidine containing dipeptide. Biochem Int. 1987;15(6):1105-13.
- Boldyrev AA, Aldini G, Derave W. Physiology and pathophysiology of carnosine. Physiol Rev. 2013;93(4):1803-45.
- Available at: http://www.lifeextension.com/magazine/2006/1/awsi/Page-01. Accessed October 9, 2017.
- Quinn PJ, Boldyrev AA, Formazuyk VE. Carnosine: its properties, functions and potential therapeutic applications. Mol Aspects Med. 1992;13(5):379-444.
- Attanasio F, Cataldo S, Fisichella S, et al. Protective effects of L- and D-carnosine on alpha-crystallin amyloid fibril formation: implications for cataract disease. Biochemistry. 2009;48(27):6522-31.
- Williams DL, Munday P. The effect of a topical antioxidant formulation including N-acetyl carnosine on canine cataract: a preliminary study. Vet Ophthalmol. 2006;9(5):311-6.
- Yan H, Guo Y, Zhang J, et al. Effect of carnosine, aminoguanidine, and aspirin drops on the prevention of cataracts in diabetic rats. Mol Vis. 2008;14:2282-91.
- Lopez-Otin C, Blasco MA, Partridge L, et al. The hallmarks of aging. Cell. 2013;153(6):1194-217.
- Gul A, Rahman MA, Hasnain SN. Role of fructose concentration on cataractogenesis in senile diabetic and non-diabetic patients. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2009;247(6):809-14.
- Gul A, Rahman MA, Salim A, et al. Advanced glycation end products in senile diabetic and nondiabetic patients with cataract. J Diabetes Complications. 2009;23(5):343-8.
- Hashim Z, Zarina S. Advanced glycation end products in diabetic and non-diabetic human subjects suffering from cataract. Age (Dordr). 2011;33(3):377-84.
- Javadi MA, Zarei-Ghanavati S. Cataracts in diabetic patients: a review article. J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2008;3(1):52-65.
- Karumanchi DK, Karunaratne N, Lurio L, et al. Non-enzymatic glycation of alpha-crystallin as an in vitro model for aging, diabetes and degenerative diseases. Amino Acids. 2015;47(12):2601-8.
- Oimomi M, Maeda Y, Hata F, et al. Glycation of cataractous lens in non-diabetic senile subjects and in diabetic patients. Exp Eye Res. 1988;46(3):415-20.
- Pokupec R, Kalauz M, Turk N, et al. Advanced glycation endproducts in human diabetic and non-diabetic cataractous lenses. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2003;241(5):378-84.
- Ramalho JS, Marques C, Pereira PC, et al. Role of glycation in human lens protein structure change. Eur J Ophthalmol. 1996;6(2):155-61.
- Sadowska-Bartosz I, Bartosz G. Effect of glycation inhibitors on aging and age-related diseases. Mech Ageing Dev. 2016;160:1-18.
- Singh VP, Bali A, Singh N, et al. Advanced glycation end products and diabetic complications. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2014;18(1):1-14.
- Moreau KL, King JA. Protein misfolding and aggregation in cataract disease and prospects for prevention. Trends Mol Med. 2012;18(5):273-82.
- Cadore EL, Izquierdo M. Exercise interventions in polypathological aging patients that coexist with diabetes mellitus: improving functional status and quality of life. Age (Dordr). 2015;37(3):64.
- Monickaraj F, Aravind S, Gokulakrishnan K, et al. Accelerated aging as evidenced by increased telomere shortening and mitochondrial DNA depletion in patients with type 2 diabetes. Mol Cell Biochem. 2012;365(1-2):343-50.
- Prevost G, Bulckaen H, Gaxatte C, et al. Structural modifications in the arterial wall during physiological aging and as a result of diabetes mellitus in a mouse model: are the changes comparable? Diabetes Metab. 2011;37(2):106-11.
- Takeuchi A, Matsushima E, Kato M, et al. Characteristics of neuropsychological functions in inpatients with poorly-controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Investig. 2012;3(3):325-30.
- Babizhayev MA. Analysis of lipid peroxidation and electron microscopic survey of maturation stages during human cataractogenesis: pharmacokinetic assay of Can-C N-acetylcarnosine prodrug lubricant eye drops for cataract prevention. Drugs R D. 2005;6(6):345-69.
- Babizhayev MA. Rejuvenation of visual functions in older adult drivers and drivers with cataract during a short-term administration of N-acetylcarnosine lubricant eye drops. Rejuvenation Res. 2004;7(3):186-98.
- Dubois VD, Bastawrous A. N-acetylcarnosine (NAC) drops for age-related cataract. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;2:CD009493.
- Ma Z, Yao W, Chan CC, et al. Human betaA3/A1-crystallin splicing mutation causes cataracts by activating the unfolded protein response and inducing apoptosis in differentiating lens fiber cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016;1862(6):1214-27.
- Watson GW, Andley UP. Activation of the unfolded protein response by a cataract-associated alphaA-crystallin mutation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;401(2):192-6.
- Zhang Q, Ames JM, Smith RD, et al. A perspective on the Maillard reaction and the analysis of protein glycation by mass spectrometry: probing the pathogenesis of chronic disease. J Proteome Res. 2009;8(2):754-69.
- Derham BK, Harding JJ. Alpha-crystallin as a molecular chaperone. Prog Retin Eye Res. 1999;18(4):463-509.
- Derham BK, Harding JJ. Effects of modifications of alpha-crystallin on its chaperone and other properties. Biochem J. 2002;364(Pt 3):711-7.
- Liang JN, Chylack LT, Jr. Spectroscopic study on the effects of nonenzymatic glycation in human alpha-crystallin. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1987;28(5):790-4.
- Abdelkader H, Longman M, Alany RG, et al. On the Anticataractogenic Effects of L-Carnosine: Is It Best Described as an Antioxidant, Metal-Chelating Agent or Glycation Inhibitor? Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:3240261.
- Babizhayev MA, Burke L, Micans P, et al. N-Acetylcarnosine sustained drug delivery eye drops to control the signs of ageless vision: glare sensitivity, cataract amelioration and quality of vision currently available treatment for the challenging 50,000-patient population. Clin Interv Aging. 2009;4:31-50.
- Babizhayev MA, Kasus-Jacobi A. State of the art clinical efficacy and safety evaluation of N-acetylcarnosine dipeptide ophthalmic prodrug. Principles for the delivery, self-bioactivation, molecular targets and interaction with a highly evolved histidyl-hydrazide structure in the treatment and therapeutic management of a group of sight-threatening eye diseases. Curr Clin Pharmacol. 2009;4(1): 4-37.
- Babizhayev MA, Guiotto A, Kasus-Jacobi A. N-Acetylcarnosine and histidyl-hydrazide are potent agents for multitargeted ophthalmic therapy of senile cataracts and diabetic ocular complications. J Drug Target. 2009;17(1):36-63.
- Allen D, Vasavada A. Cataract and surgery for cataract. BMJ. 2006;333(7559):128-32.
- Gimbel HV, Dardzhikova AA. Consequences of waiting for cataract surgery. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2011;22(1):28-30.