Oral Probiotics Combat Gum Disease
 In the era of the COVID-19 pandemic, caring for oral hygiene seems to be particularly important. The human mouth is teeming with bacteria that can cause dental cavities and more serious gingivitis and periodontitis. Even good oral hygiene habits of brushing and flossing twice a day might not be enough to ward them off.
In the era of the COVID-19 pandemic, caring for oral hygiene seems to be particularly important. The human mouth is teeming with bacteria that can cause dental cavities and more serious gingivitis and periodontitis. Even good oral hygiene habits of brushing and flossing twice a day might not be enough to ward them off.
Nearly a third of US adults have untreated tooth decay, and nearly half of those 30 and older have periodontal (gum) disease.1,2
Gum disease can be serious. As it progresses, it can lead to tooth loss, as well as inflammation that accelerates degenerative aging processes.3 Gum disease can lead to heart problems, cancer, Alzheimer’s, lung and kidney disorders, and more.4-14
Scientists looking for a solution to gum disease and tooth decay have discovered an innovative way to reduce the risk through targeted oral probiotic lozenges.
The Oral Microbiome
The natural community of microbes living in the mouth is called the oral microbiome. A healthy microbiome supports and protects the delicate mucous membranes as well as the surface of the teeth themselves.
When this community becomes disrupted and out of balance–whether by poor diet, lifestyle, drugs, or disease—it results in a state of microbial imbalance (called dysbiosis) that wreaks havoc on the normal immune system response.
Dysbiosis leads to numerous problems in the mouth, including cavities that arise from excessive acid-producing bacteria, and gum disease that contributes to tooth loss as well as inflammatory diseases throughout the body.
The need to restore a healthy oral microbiome led scientists to identify two strains of good bacteria that can combat gum disease on two fronts. The first one, L. plantarum L-137, boosts oral immune function and promotes healing. The second one, S. salivarius M18, kills harmful bacteria that live in the mouth, allowing itself to flourish.15-17
This two-pronged approach to gum disease prevention supports a healthy, balanced microbiome in the mouth, one that actively resists disease while promoting healing.
Harnessing Natural Immune Responses
 One of the key problems with an imbalanced oral microbiome is that it reduces the mouth’s natural immune-fighting abilities. This leaves us vulnerable to infections by bacteria that cause gum disease, such as Porphyromonas gingivalis.
One of the key problems with an imbalanced oral microbiome is that it reduces the mouth’s natural immune-fighting abilities. This leaves us vulnerable to infections by bacteria that cause gum disease, such as Porphyromonas gingivalis.
Making matters worse, P. gingivalis diminishes the mouth’s immune system even further by downregulating protective IL-12 and upregulating pro-inflammatory IL-6, creating a vicious cycle that makes it nearly impossible for the body to heal itself.18-20
In order to counteract this disease-promoting cycle, scientists searched for a way to boost local immune function. They found their answer in the harmless bacterium Lactobacillus plantarum, strain L-137.17 When killed by heat treatment, this strain of L. plantarum has been found to increase production of the protective IL-12.
Treating periodontitis patients with this immune-boosting bacterium helps to overcome the impaired immune function in their mouths that occurs as a result of P. gingivalis. This assists in restoring the body’s natural oral immune response, which in turn promotes healing of the diseased, inflamed gums.
In other words, L. plantarum essentially plugs the immune system “hole” induced by evasive P. gingivalis and other bacteria, allowing our bodies to naturally resist gum disease.17
The impact of this was seen in a clinical trial of people with chronic periodontitis.
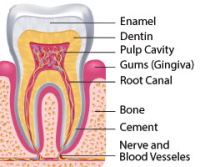 Tooth and gum disease are often-overlooked major contributors to failing health as we age.
Tooth and gum disease are often-overlooked major contributors to failing health as we age.- In addition to taking a toll on functions of the mouth, these conditions predispose us to heart, lung, brain, liver, and other age-related disorders.
- A balanced oral microbiome helps maintain a state of disease-resistance.
- An imbalanced, or dysbiotic, microbiome invites disaster by changing the elaborate natural immune and bacterial defenses against oral disease.
- Balancing a dysbiotic oral microbiome can restore natural disease resistance.
- HT-L. plantarum L-137 is a heat-treated strain of common Lactobacillus bacteria capable of inducing pro-healing cytokines in the mouth and boosting local immunity.
- S. salivarius M18 is a living probiotic strain that is armed with powerful lantibiotics that kill harmful bacteria.
- Adding these healthy bacteria to a regular routine of brushing and flossing can help make the mouth a safe place for protective microbes, which produces benefits throughout the body.
Clinical Trial
Researchers conducted a randomized trial that included 39 people with chronic periodontitis.17 The subjects were randomly assigned to receive either a placebo or the L. plantarum L-137 supplement for 12 weeks.
Over the course of 12 weeks, researchers measured the probing pocket depth, which is the distance from the gum line to the bottom of the tiny “pocket” between gum and tooth root.17 A normal, healthy gum pocket is 3 mm deep or less, and a depth of 4 mm or more defines periodontitis.21 Deeper pockets are a clinical measure of periodontal disease.
After 12 weeks, subjects supplementing with L. plantarum L-137 had a 64% greater improvement in pocket depth compared with placebo recipients.17
This remarkable study showed that it’s possible to improve periodontal disease through modulation of the oral immune system.
Improving pocket depth is one piece of the puzzle. It is equally important to restore balance to the mouth’s microbial community. By doing so, we can prevent immune dysfunction and the resulting inflammatory changes before they set in. That’s where an oral probiotic called S. salivarius M18 comes to the rescue.
 Periodontal (gum) disease can be painful, disfiguring, and even disabling when tooth loss and jawbone resorption occur.
Periodontal (gum) disease can be painful, disfiguring, and even disabling when tooth loss and jawbone resorption occur.
But new science is showing that periodontal disease has far-reaching consequences that extend into most body systems, largely the result of inflammatory changes and other signaling pathway disruptions throughout the body.
Gum disease is now associated with disorders of the brain, heart, lungs, kidney, liver, and blood vessels—all of which promote aging and shorten lifespan.7-14
The good news is that reducing bacteria-laden plaque results in significant reductions in total-body inflammation.29 This means that improving our tooth and gum health is vital not just for those oral structures, but also to preserve our health in practically all body systems.
A Well-Armed Probiotic Oral Defense System
 A disease-resistant oral microbiome includes a wide variety of microbes that provide important biological functions. A dysbiotic microbiome is one in which one or several harmful strains dominate, suppressing other beneficial organisms and creating a disease-permissive environment.
A disease-resistant oral microbiome includes a wide variety of microbes that provide important biological functions. A dysbiotic microbiome is one in which one or several harmful strains dominate, suppressing other beneficial organisms and creating a disease-permissive environment.
What the research is proving is that in order to restore oral health and avoid problems such as gum disease, it is necessary to support the colonization and growth of beneficial organisms.22
The helpful organisms compete with the “bad guys,” cutting their populations down to size and allowing a wider range of beneficial microbes to succeed.
S. salivarius M18 is one of the “good guys.” It competes with dangerous oral bacteria that cause or exacerbate periodontal disease, and has been shown to improve parameters of gingivitis and periodontitis.15,16
A randomized, controlled trial was conducted to determine the impact of S. salivarius M18 treatment on some of the most important clinical parameters of oral and gingival (gum) health.23 The study included men and women aged 20-60 years with moderate or severe gingivitis (gingival index score of 2 or 3), and moderate periodontitis (less than 6 mm probing pocket depth).
Half of the subjects received no treatment, and half received lozenges with 200 million S. salivarius M18 daily after brushing. The subjects took the lozenges for 30 days, and the researchers observed them for an additional 30 days to determine if the benefits would continue even after the subjects stopped taking the probiotic.
The results of the S. salivarius M18 group were favorable for all four measurements compared to the control group:23
- The mean plaque index score was reduced by 44% on day 30 (the last day of treatment), and by 37% on day 60.
- The mean gingival index score was reduced by 42% on day 30, and by 35% on day 60.
- The modified sulcus bleeding index scores were reduced by 53% on day 30, and by 51% on day 60.
- Finally, probing pocket depth measurements were reduced by 20% on day 30, and by 22% on day 60.
Of note, the lowest scores for each index in the S. salivarius M18 group indicated a return to near-normal values of less than 1 for plaque index, gingival index, and modified sulcus bleeding index, and a probing pocket depth of just over 3 mm. These values remained markedly abnormal in control subjects.23
This study demonstrated the ability of the probiotic lozenge not only to significantly improve all four of the most important parameters of periodontal health, but also to continue working long after supplementation ended.
Previous clinical studies lend additional support to the use of S. salivarius M18 for oral health. In one, 88% of S. salivarius M18 recipients maintained plaque scores lower than their baseline, pretreatment values at the end of a 3-month treatment period, compared with just 44% of placebo recipients.15
 Dysbiosis (an imbalanced microbiome) in the mouth induces profound dysfunction of the immune system that is designed to protect the teeth and gums, and has two major effects on oral health:
Dysbiosis (an imbalanced microbiome) in the mouth induces profound dysfunction of the immune system that is designed to protect the teeth and gums, and has two major effects on oral health:
- First, oral dysbiosis and pathogenic bacteria (e.g., P. gingivalis) are associated with increased activity of inflammatory cytokines (signaling molecules), notably IL-6.18
- Second, dysbiosis reduces production of IL-12, a regulatory cytokine that supports healthy immune responses and healing after inflammation. This altered immune response contributes to persistent inflammation and slowed healing, a situation that the destructive microbes can exploit to promote their own growth.18,30,31
IL-12 production decreases with aging, leaving a “hole” in immune responses in the mouth.32 This allows organisms like P. gingivalis to evade the immune system and become overgrown, and it ultimately causes gum disease.30
Making matters worse, P. gingivalis itself also impairs host immune responses, specifically reducing beneficial IL-12 and upregulating pro-inflammatory IL-6.18-20,30 This permits overgrowth of P. gingivalis and other infection- and inflammation-producing microbes.33
Additionally, when IL-6 levels remain high, and IL-12 levels low, it is nearly impossible for inflammation of the gums to resolve on its own. This leads to a chronic inflammatory state that eventually erodes the bony tooth socket, ultimately producing tooth loss.10,18-20
In an elegant but destructive process, P. gingivalis releases chemical fragments that suppress the effects of certain immune cells, “disguising” itself as a normal, beneficial organism, while simultaneously invading the host’s tissues and suppressing its immune response towards other bacterial species as well.
How it Works
 S. salivarius M18 works by several actions to help create a healthier oral environment. Unlike many probiotic formulations, S. salivarius M18 can specifically colonize the human mouth. This results in stable, reproducing colonies of this beneficial organism even after supplementation ends.16
S. salivarius M18 works by several actions to help create a healthier oral environment. Unlike many probiotic formulations, S. salivarius M18 can specifically colonize the human mouth. This results in stable, reproducing colonies of this beneficial organism even after supplementation ends.16
S. salivarius M18 has also been shown to compete effectively with bacteria (such as Streptococcus mutans) that can cause cavities, helping to support healthy teeth and gums.15
S. salivarius M18 is an abundant producer of bacteria-suppressing weapons called bacteriocins.
Bacteriocins function similar to antibiotics, but are entirely natural, and appear to act only at the local level between different bacterial strains.24
The specific bacteriocins that S. salivarius M18 produces are in a class called lantibiotics that use a mode of action that literally creates a hole, or pore, in the target organism’s cell membrane leading to its destruction.25,26 In this fashion, S. salivarius M18 has been shown to inhibit the growth of several well-known tooth and gum disease-producing organisms, including S. mutans, S. sobrinus, and Actinomyces naeslundii.15,24,27,28
In addition to its targeting of disease-causing organisms, S. salivarius M18 produces enzymes that help break down dental plaque, which is a main cause of tooth decay and gum disease. S. salivarius M18 also helps generate a neutral pH in the mouth that supports healthful bacteria, further balancing the oral microbiome and reducing disease risk.15
An additional research finding is that S. salivarius M18 reduces the presence of the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-6 which is associated with periodontal disease.15 This complements a beneficial overlap with the immune-modulating features of L. plantarum L-137, providing added protection against chronic gum inflammation.
 All that probing and poking around in your mouth at the dentist’s is no fun. But the dentist or hygienist is in fact looking carefully at multiple features of teeth and gums.
All that probing and poking around in your mouth at the dentist’s is no fun. But the dentist or hygienist is in fact looking carefully at multiple features of teeth and gums.
These have been standardized into several scores useful for measuring gum health, as well as for determining the best treatment option.
Those used in studies cited in this article are:
- The Plaque Index score: a zero to 3 rating, with zero being no plaque, and 3 being an abundance of plaque that extends below the gum line on the teeth.34
- The Gingival Index score: a zero to 3 rating, with zero being normal gums, and 3 indicating severe inflammation with swelling, ulceration, and a tendency to spontaneous bleeding.34
- The Modified Sulcus Bleeding Index score: a zero to 3 rating, with zero being no bleeding with gentle dental probing and 3 being ready bleeding, change of color, and gum swelling.35
- Probing Pocket Depth: using a calibrated probe marked in millimeters, the dentist or hygienist measures the depth of the pocket between the tooth root and the gum. Generally, the deeper the pocket, the worse the gum disease, with pockets 3 mm or less in depth considered normal, while those deeper than 4 mm indicate periodontitis.21,36
Summary
Gum diseases are rampant, especially as we age past 30 years.
Tooth brushing and flossing are important, but are insufficient to restore a damaged oral microbiome to its natural, disease-resistant state.
Recent advances in the understanding of beneficial bacteria (probiotics) reveal a two-pronged approach to restoring a balanced microbiome and rejuvenating healthy immune function in the mouth.
L. plantarum L-137 is a heat-treated preparation of beneficial L. plantarum bacteria that boosts oral immune function, reduces inflammation, and promotes healing.
S. salivarius M18 is a proven oral probiotic capable of colonizing the human mouth, where it kills harmful bacteria.
These two probiotics, when taken as a daily lozenge, can work together to enhance not only oral, but total-body health.
Material used with permission of Life Extension. All rights reserved.
-
Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/OralHealth/children_adults/adults.htm. Accessed October 25, 2016.
-
Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/oralhealth/periodontal_disease/. Accessed December 8, 2016.
-
Sampaio-Maia B, Caldas IM, Pereira ML, et al. The Oral Microbiome in Health and Its Implication in Oral and Systemic Diseases. Adv Appl Microbiol. 2016;97:171-210.
-
Saffi MA, Furtado MV, Polanczyk CA, et al. Relationship between vascular endothelium and periodontal disease in atherosclerotic lesions: Review article. World J Cardiol. 2015;7(1):26-30.
-
Yao QW, Zhou DS, Peng HJ, et al. Association of periodontal disease with oral cancer: a meta-analysis. Tumour Biol. 2014;35(7):7073-7.
-
Watts A, Crimmins EM, Gatz M. Inflammation as a potential mediator for the association between periodontal disease and Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2008;4(5):865-76.
-
Kamer AR, Pirraglia E, Tsui W, et al. Periodontal disease associates with higher brain amyloid load in normal elderly. Neurobiol Aging. 2015;36(2):627-33.
-
Prasanna SJ. Causal relationship between periodontitis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2011;15(4):359-65.
-
Fisher MA, Taylor GW, West BT, et al. Bidirectional relationship between chronic kidney and periodontal disease: a study using structural equation modeling. Kidney Int. 2011;79(3):347-55.
-
Hajishengallis G. Periodontitis: from microbial immune subversion to systemic inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2015;15(1):30-44.
-
Humphrey LL, Fu R, Buckley DI, et al. Periodontal disease and coronary heart disease incidence: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Gen Intern Med. 2008;23(12):2079-86.
-
Liu Z, Zhang W, Zhang J, et al. Oral hygiene, periodontal health and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbations. J Clin Periodontol. 2012;39(1):45-52.
-
Scannapieco FA, Bush RB, Paju S. Associations between periodontal disease and risk for nosocomial bacterial pneumonia and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. A systematic review. Ann Periodontol. 2003;8(1):54-69.
-
Kshirsagar AV, Moss KL, Elter JR, et al. Periodontal disease is associated with renal insufficiency in the Atherosclerosis Risk In Communities (ARIC) study. Am J Kidney Dis. 2005;45(4):650-7.
-
Burton JP, Drummond BK, Chilcott CN, et al. Influence of the probiotic Streptococcus salivarius strain M18 on indices of dental health in children: a randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Med Microbiol. 2013;62(Pt 6):875-84.
-
Burton JP, Wescombe PA, Macklaim JM, et al. Persistence of the oral probiotic Streptococcus salivarius M18 is dose dependent and megaplasmid transfer can augment their bacteriocin production and adhesion characteristics. PLoS One. 2013;8(6):e65991.
-
Iwasaki K, Maeda K, Hidaka K, et al. Daily Intake of Heat-killed Lactobacillus plantarum L-137 Decreases the Probing Depth in Patients Undergoing Supportive Periodontal Therapy. Oral Health Prev Dent. 2016;14(3):207-14.
-
Liang S, Krauss JL, Domon H, et al. The C5a receptor impairs IL-12-dependent clearance of Porphyromonas gingivalis and is required for induction of periodontal bone loss. J Immunol. 2011;186(2):869-77.
-
Johnson RB, Serio FG. Interleukin-18 concentrations and the pathogenesis of periodontal disease. J Periodontol. 2005;76(5):785-90.
-
Gemmell E, Seymour GJ. Immunoregulatory control of Th1/Th2 cytokine profiles in periodontal disease. Periodontol 2000. 2004;35:21-41.
-
Available at: http://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/dental-disorders/periodontal-disorders/periodontitis. Accessed February 1, 2017.
-
Bonifait L, Chandad F, Grenier D. Probiotics for oral health: myth or reality? J Can Dent Assoc. 2009;75(8):585-90.
-
Scariya L, Nagarathna DV, Varghese M. Probiotics in Periodontal Therapy. Int J Pharm Bio. 2015 Jan;6(1):242-50.
-
Wescombe PA, Upton M, Renault P, et al. Salivaricin 9, a new lantibiotic produced by Streptococcus salivarius. Microbiology. 2011;157(Pt 5):1290-9.
-
Bierbaum G, Sahl HG. Lantibiotics: mode of action, biosynthesis and bioengineering. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2009;10(1):2-18.
-
Islam MR, Nagao J, Zendo T, et al. Antimicrobial mechanism of lantibiotics. Biochem Soc Trans. 2012;40(6):1528-33.
-
Wescombe PA, Burton JP, Cadieux PA, et al. Megaplasmids encode differing combinations of lantibiotics in Streptococcus salivarius. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2006;90(3):269-80.
-
Wescombe PA, Upton M, Dierksen KP, et al. Production of the lantibiotic salivaricin A and its variants by oral streptococci and use of a specific induction assay to detect their presence in human saliva. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006;72(2):1459-66.
-
Fasula K, Evans CA, Boyd L, et al. Randomized trial of Plaque identifying Toothpaste: Dental Plaque and Inflammation. Am J Med. 2016.
-
Hajishengallis G, Shakhatreh MA, Wang M, et al. Complement receptor 3 blockade promotes IL-12-mediated clearance of Porphyromonas gingivalis and negates its virulence in vivo. J Immunol. 2007;179(4):2359-67.
-
Li L, Hsu HC, Stockard CR, et al. IL-12 inhibits thymic involution by enhancing IL-7- and IL-2-induced thymocyte proliferation. J Immunol. 2004;172(5):2909-16.
-
Banerjee C, Ulloor J, Dillon EL, et al. Identification of serum biomarkers for aging and anabolic response. Immun Ageing. 2011;8(1):5.
-
Costalonga M, Herzberg MC. The oral microbiome and the immunobiology of periodontal disease and caries. Immunol Lett. 2014;162(2 Pt A):22-38.
-
Loe H. The Gingival Index, the Plaque Index and the Retention Index Systems. J Periodontol. 1967;38(6):Suppl:610-6.
 The human mouth is teeming with bacteria that can cause dental cavities and more serious gingivitis and periodontitis. Even good oral hygiene habits of brushing and flossing twice a day might not be enough to ward them off.
The human mouth is teeming with bacteria that can cause dental cavities and more serious gingivitis and periodontitis. Even good oral hygiene habits of brushing and flossing twice a day might not be enough to ward them off.Nearly a third of US adults have untreated tooth decay, and nearly half of those 30 and older have periodontal (gum) disease.1,2
Gum disease can be serious. As it progresses, it can lead to tooth loss, as well as inflammation that accelerates degenerative aging processes.3 Gum disease can lead to heart problems, cancer, Alzheimer’s, lung and kidney disorders, and more.4-14
Scientists looking for a solution to gum disease and tooth decay have discovered an innovative way to reduce the risk through targeted oral probiotic lozenges.
The Oral Microbiome
The natural community of microbes living in the mouth is called the oral microbiome. A healthy microbiome supports and protects the delicate mucous membranes as well as the surface of the teeth themselves.
When this community becomes disrupted and out of balance–whether by poor diet, lifestyle, drugs, or disease—it results in a state of microbial imbalance (called dysbiosis) that wreaks havoc on the normal immune system response.
Dysbiosis leads to numerous problems in the mouth, including cavities that arise from excessive acid-producing bacteria, and gum disease that contributes to tooth loss as well as inflammatory diseases throughout the body.
The need to restore a healthy oral microbiome led scientists to identify two strains of good bacteria that can combat gum disease on two fronts. The first one, L. plantarum L-137, boosts oral immune function and promotes healing. The second one, S. salivarius M18, kills harmful bacteria that live in the mouth, allowing itself to flourish.15-17
This two-pronged approach to gum disease prevention supports a healthy, balanced microbiome in the mouth, one that actively resists disease while promoting healing.
Harnessing Natural Immune Responses
 One of the key problems with an imbalanced oral microbiome is that it reduces the mouth’s natural immune-fighting abilities. This leaves us vulnerable to infections by bacteria that cause gum disease, such as Porphyromonas gingivalis.
One of the key problems with an imbalanced oral microbiome is that it reduces the mouth’s natural immune-fighting abilities. This leaves us vulnerable to infections by bacteria that cause gum disease, such as Porphyromonas gingivalis.Making matters worse, P. gingivalis diminishes the mouth’s immune system even further by downregulating protective IL-12 and upregulating pro-inflammatory IL-6, creating a vicious cycle that makes it nearly impossible for the body to heal itself.18-20
In order to counteract this disease-promoting cycle, scientists searched for a way to boost local immune function. They found their answer in the harmless bacterium Lactobacillus plantarum, strain L-137.17 When killed by heat treatment, this strain of L. plantarum has been found to increase production of the protective IL-12.
Treating periodontitis patients with this immune-boosting bacterium helps to overcome the impaired immune function in their mouths that occurs as a result of P. gingivalis. This assists in restoring the body’s natural oral immune response, which in turn promotes healing of the diseased, inflamed gums.
In other words, L. plantarum essentially plugs the immune system “hole” induced by evasive P. gingivalis and other bacteria, allowing our bodies to naturally resist gum disease.17
The impact of this was seen in a clinical trial of people with chronic periodontitis.
What You Need to Know Probiotic Combats Gum Disease Tooth and gum disease are often-overlooked major contributors to failing health as we age.
Tooth and gum disease are often-overlooked major contributors to failing health as we age.- In addition to taking a toll on functions of the mouth, these conditions predispose us to heart, lung, brain, liver, and other age-related disorders.
- A balanced oral microbiome helps maintain a state of disease-resistance.
- An imbalanced, or dysbiotic, microbiome invites disaster by changing the elaborate natural immune and bacterial defenses against oral disease.
- Balancing a dysbiotic oral microbiome can restore natural disease resistance.
- HT-L. plantarum L-137 is a heat-treated strain of common Lactobacillus bacteria capable of inducing pro-healing cytokines in the mouth and boosting local immunity.
- S. salivarius M18 is a living probiotic strain that is armed with powerful lantibiotics that kill harmful bacteria.
- Adding these healthy bacteria to a regular routine of brushing and flossing can help make the mouth a safe place for protective microbes, which produces benefits throughout the body.
Clinical Trial
Researchers conducted a randomized trial that included 39 people with chronic periodontitis.17 The subjects were randomly assigned to receive either a placebo or the L. plantarum L-137 supplement for 12 weeks.
Over the course of 12 weeks, researchers measured the probing pocket depth, which is the distance from the gum line to the bottom of the tiny “pocket” between gum and tooth root.17 A normal, healthy gum pocket is 3 mm deep or less, and a depth of 4 mm or more defines periodontitis.21 Deeper pockets are a clinical measure of periodontal disease.
After 12 weeks, subjects supplementing with L. plantarum L-137 had a 64% greater improvement in pocket depth compared with placebo recipients.17
This remarkable study showed that it’s possible to improve periodontal disease through modulation of the oral immune system.
Improving pocket depth is one piece of the puzzle. It is equally important to restore balance to the mouth’s microbial community. By doing so, we can prevent immune dysfunction and the resulting inflammatory changes before they set in. That’s where an oral probiotic called S. salivarius M18 comes to the rescue.
Whole-Body Effects of Periodontal Disease Periodontal (gum) disease can be painful, disfiguring, and even disabling when tooth loss and jawbone resorption occur.
Periodontal (gum) disease can be painful, disfiguring, and even disabling when tooth loss and jawbone resorption occur.But new science is showing that periodontal disease has far-reaching consequences that extend into most body systems, largely the result of inflammatory changes and other signaling pathway disruptions throughout the body.
Gum disease is now associated with disorders of the brain, heart, lungs, kidney, liver, and blood vessels—all of which promote aging and shorten lifespan.7-14
The good news is that reducing bacteria-laden plaque results in significant reductions in total-body inflammation.29 This means that improving our tooth and gum health is vital not just for those oral structures, but also to preserve our health in practically all body systems.
A Well-Armed Probiotic Oral Defense System
 A disease-resistant oral microbiome includes a wide variety of microbes that provide important biological functions. A dysbiotic microbiome is one in which one or several harmful strains dominate, suppressing other beneficial organisms and creating a disease-permissive environment.
A disease-resistant oral microbiome includes a wide variety of microbes that provide important biological functions. A dysbiotic microbiome is one in which one or several harmful strains dominate, suppressing other beneficial organisms and creating a disease-permissive environment.What the research is proving is that in order to restore oral health and avoid problems such as gum disease, it is necessary to support the colonization and growth of beneficial organisms.22
The helpful organisms compete with the “bad guys,” cutting their populations down to size and allowing a wider range of beneficial microbes to succeed.
S. salivarius M18 is one of the “good guys.” It competes with dangerous oral bacteria that cause or exacerbate periodontal disease, and has been shown to improve parameters of gingivitis and periodontitis.15,16
A randomized, controlled trial was conducted to determine the impact of S. salivarius M18 treatment on some of the most important clinical parameters of oral and gingival (gum) health.23 The study included men and women aged 20-60 years with moderate or severe gingivitis (gingival index score of 2 or 3), and moderate periodontitis (less than 6 mm probing pocket depth).
Half of the subjects received no treatment, and half received lozenges with 200 million S. salivarius M18 daily after brushing. The subjects took the lozenges for 30 days, and the researchers observed them for an additional 30 days to determine if the benefits would continue even after the subjects stopped taking the probiotic.
The results of the S. salivarius M18 group were favorable for all four measurements compared to the control group:23
- The mean plaque index score was reduced by 44% on day 30 (the last day of treatment), and by 37% on day 60.
- The mean gingival index score was reduced by 42% on day 30, and by 35% on day 60.
- The modified sulcus bleeding index scores were reduced by 53% on day 30, and by 51% on day 60.
- Finally, probing pocket depth measurements were reduced by 20% on day 30, and by 22% on day 60.
Of note, the lowest scores for each index in the S. salivarius M18 group indicated a return to near-normal values of less than 1 for plaque index, gingival index, and modified sulcus bleeding index, and a probing pocket depth of just over 3 mm. These values remained markedly abnormal in control subjects.23
This study demonstrated the ability of the probiotic lozenge not only to significantly improve all four of the most important parameters of periodontal health, but also to continue working long after supplementation ended.
Previous clinical studies lend additional support to the use of S. salivarius M18 for oral health. In one, 88% of S. salivarius M18 recipients maintained plaque scores lower than their baseline, pretreatment values at the end of a 3-month treatment period, compared with just 44% of placebo recipients.15
Gum Disease and the Adult Immune System Dysbiosis (an imbalanced microbiome) in the mouth induces profound dysfunction of the immune system that is designed to protect the teeth and gums, and has two major effects on oral health:
Dysbiosis (an imbalanced microbiome) in the mouth induces profound dysfunction of the immune system that is designed to protect the teeth and gums, and has two major effects on oral health:- First, oral dysbiosis and pathogenic bacteria (e.g., P. gingivalis) are associated with increased activity of inflammatory cytokines (signaling molecules), notably IL-6.18
- Second, dysbiosis reduces production of IL-12, a regulatory cytokine that supports healthy immune responses and healing after inflammation. This altered immune response contributes to persistent inflammation and slowed healing, a situation that the destructive microbes can exploit to promote their own growth.18,30,31
IL-12 production decreases with aging, leaving a “hole” in immune responses in the mouth.32 This allows organisms like P. gingivalis to evade the immune system and become overgrown, and it ultimately causes gum disease.30
Making matters worse, P. gingivalis itself also impairs host immune responses, specifically reducing beneficial IL-12 and upregulating pro-inflammatory IL-6.18-20,30 This permits overgrowth of P. gingivalis and other infection- and inflammation-producing microbes.33
Additionally, when IL-6 levels remain high, and IL-12 levels low, it is nearly impossible for inflammation of the gums to resolve on its own. This leads to a chronic inflammatory state that eventually erodes the bony tooth socket, ultimately producing tooth loss.10,18-20
In an elegant but destructive process, P. gingivalis releases chemical fragments that suppress the effects of certain immune cells, “disguising” itself as a normal, beneficial organism, while simultaneously invading the host’s tissues and suppressing its immune response towards other bacterial species as well.
How it Works
 S. salivarius M18 works by several actions to help create a healthier oral environment. Unlike many probiotic formulations, S. salivarius M18 can specifically colonize the human mouth. This results in stable, reproducing colonies of this beneficial organism even after supplementation ends.16
S. salivarius M18 works by several actions to help create a healthier oral environment. Unlike many probiotic formulations, S. salivarius M18 can specifically colonize the human mouth. This results in stable, reproducing colonies of this beneficial organism even after supplementation ends.16S. salivarius M18 has also been shown to compete effectively with bacteria (such as Streptococcus mutans) that can cause cavities, helping to support healthy teeth and gums.15
S. salivarius M18 is an abundant producer of bacteria-suppressing weapons called bacteriocins.
Bacteriocins function similar to antibiotics, but are entirely natural, and appear to act only at the local level between different bacterial strains.24
The specific bacteriocins that S. salivarius M18 produces are in a class called lantibiotics that use a mode of action that literally creates a hole, or pore, in the target organism’s cell membrane leading to its destruction.25,26 In this fashion, S. salivarius M18 has been shown to inhibit the growth of several well-known tooth and gum disease-producing organisms, including S. mutans, S. sobrinus, and Actinomyces naeslundii.15,24,27,28
In addition to its targeting of disease-causing organisms, S. salivarius M18 produces enzymes that help break down dental plaque, which is a main cause of tooth decay and gum disease. S. salivarius M18 also helps generate a neutral pH in the mouth that supports healthful bacteria, further balancing the oral microbiome and reducing disease risk.15
An additional research finding is that S. salivarius M18 reduces the presence of the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-6 which is associated with periodontal disease.15 This complements a beneficial overlap with the immune-modulating features of L. plantarum L-137, providing added protection against chronic gum inflammation.
What Dentists Look for To Measure Gum Health
 All that probing and poking around in your mouth at the dentist’s is no fun. But the dentist or hygienist is in fact looking carefully at multiple features of teeth and gums.
All that probing and poking around in your mouth at the dentist’s is no fun. But the dentist or hygienist is in fact looking carefully at multiple features of teeth and gums.These have been standardized into several scores useful for measuring gum health, as well as for determining the best treatment option.
Those used in studies cited in this article are:
- The Plaque Index score: a zero to 3 rating, with zero being no plaque, and 3 being an abundance of plaque that extends below the gum line on the teeth.34
- The Gingival Index score: a zero to 3 rating, with zero being normal gums, and 3 indicating severe inflammation with swelling, ulceration, and a tendency to spontaneous bleeding.34
- The Modified Sulcus Bleeding Index score: a zero to 3 rating, with zero being no bleeding with gentle dental probing and 3 being ready bleeding, change of color, and gum swelling.35
- Probing Pocket Depth: using a calibrated probe marked in millimeters, the dentist or hygienist measures the depth of the pocket between the tooth root and the gum. Generally, the deeper the pocket, the worse the gum disease, with pockets 3 mm or less in depth considered normal, while those deeper than 4 mm indicate periodontitis.21,36
Summary
Gum diseases are rampant, especially as we age past 30 years.
Tooth brushing and flossing are important, but are insufficient to restore a damaged oral microbiome to its natural, disease-resistant state.
Recent advances in the understanding of beneficial bacteria (probiotics) reveal a two-pronged approach to restoring a balanced microbiome and rejuvenating healthy immune function in the mouth.
L. plantarum L-137 is a heat-treated preparation of beneficial L. plantarum bacteria that boosts oral immune function, reduces inflammation, and promotes healing.
S. salivarius M18 is a proven oral probiotic capable of colonizing the human mouth, where it kills harmful bacteria.
These two probiotics, when taken as a daily lozenge, can work together to enhance not only oral, but total-body health.
-
Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/OralHealth/children_adults/adults.htm. Accessed October 25, 2016.
-
Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/oralhealth/periodontal_disease/. Accessed December 8, 2016.
-
Sampaio-Maia B, Caldas IM, Pereira ML, et al. The Oral Microbiome in Health and Its Implication in Oral and Systemic Diseases. Adv Appl Microbiol. 2016;97:171-210.
-
Saffi MA, Furtado MV, Polanczyk CA, et al. Relationship between vascular endothelium and periodontal disease in atherosclerotic lesions: Review article. World J Cardiol. 2015;7(1):26-30.
-
Yao QW, Zhou DS, Peng HJ, et al. Association of periodontal disease with oral cancer: a meta-analysis. Tumour Biol. 2014;35(7):7073-7.
-
Watts A, Crimmins EM, Gatz M. Inflammation as a potential mediator for the association between periodontal disease and Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2008;4(5):865-76.
-
Kamer AR, Pirraglia E, Tsui W, et al. Periodontal disease associates with higher brain amyloid load in normal elderly. Neurobiol Aging. 2015;36(2):627-33.
-
Prasanna SJ. Causal relationship between periodontitis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2011;15(4):359-65.
-
Fisher MA, Taylor GW, West BT, et al. Bidirectional relationship between chronic kidney and periodontal disease: a study using structural equation modeling. Kidney Int. 2011;79(3):347-55.
-
Hajishengallis G. Periodontitis: from microbial immune subversion to systemic inflammation. <spa


